- Bitcoin miners are grappling with reduced earnings as transaction fees reach unprecedented lows.
- Increasing network difficulty and higher operational costs are posing survival challenges for smaller mining operations.
Bitcoin (BTC) miners are navigating a tough environment in 2025, as critical factors jeopardize their profitability. Notably, transaction fees have fallen to their lowest level since 2012, while network difficulty is on the rise.
The upcoming halving in 2024 is intensifying competition, causing revenues per hashing unit to swiftly diminish.
Moreover, mining revenue denominated in USD remains unstable, adding uncertainty even for established players.
As profit margins tighten, miners are compelled to enhance their operational efficiency, retire outdated equipment, or explore mergers.
With smaller enterprises at risk of exiting the market, industry consolidation appears inevitable, leaving only the most efficient and capital-rich operations to endure.
Profitability Challenges in Bitcoin Mining
The Bitcoin mining environment is confronted with considerable challenges, with various critical indicators suggesting a decrease in profitability.
The Bitcoin mempool, which monitors unconfirmed transactions, has reached its lowest levels in recent years, indicating weakened demand across the network.
This decline directly affects miners’ earnings from transaction fees, an essential component alongside block rewards.
Historically, comparable decreases in transaction activity have preceded bear markets, and this current downturn—despite the high valuation of Bitcoin—might point toward a fundamental shift within the network.
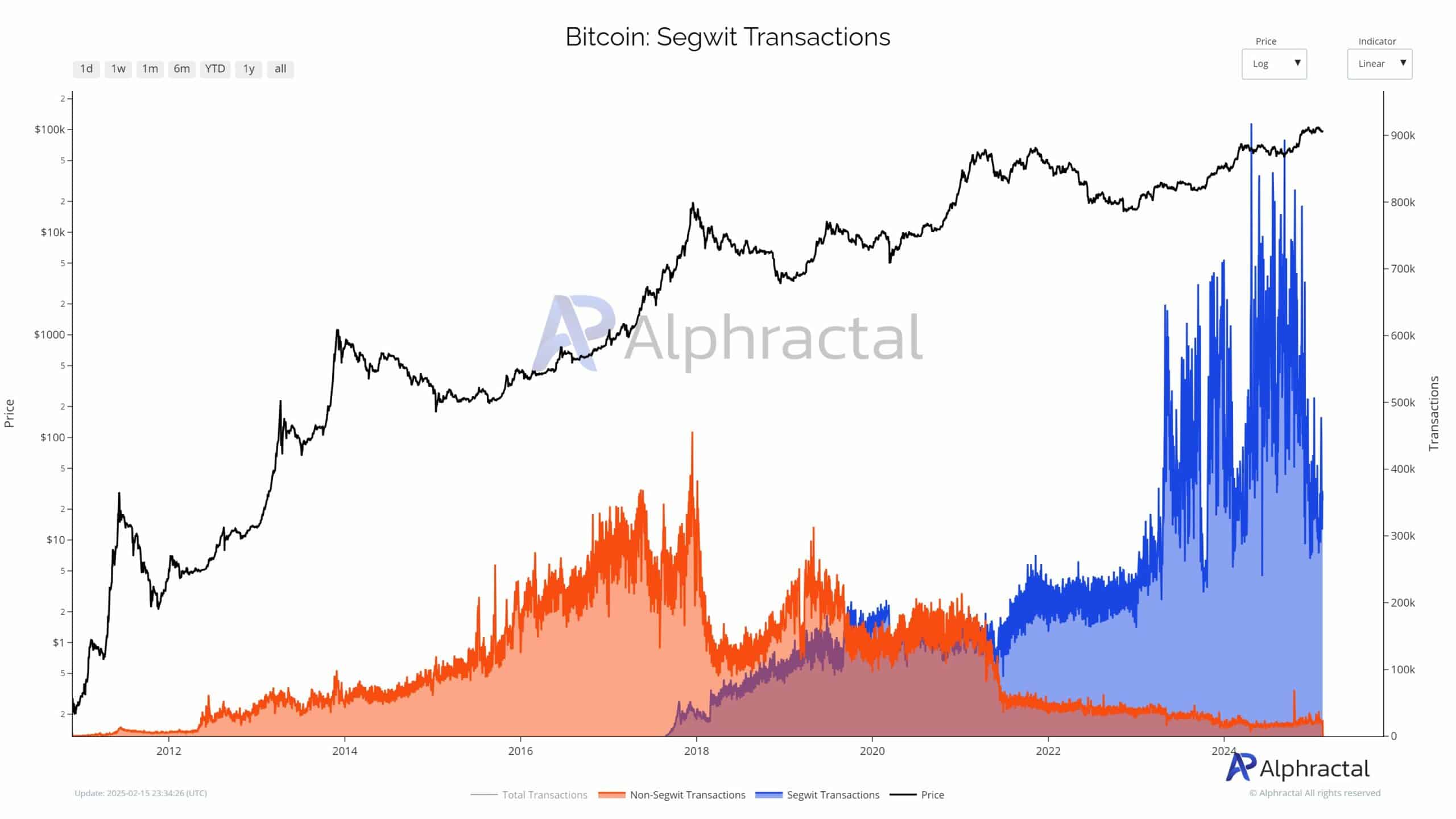
Additionally, SegWit transactions, which were previously the most efficient transaction type, are now experiencing a decline.
This trend diminishes overall network efficiency, amplifying the demand for block space and exerting further pressure on miners’ earnings.
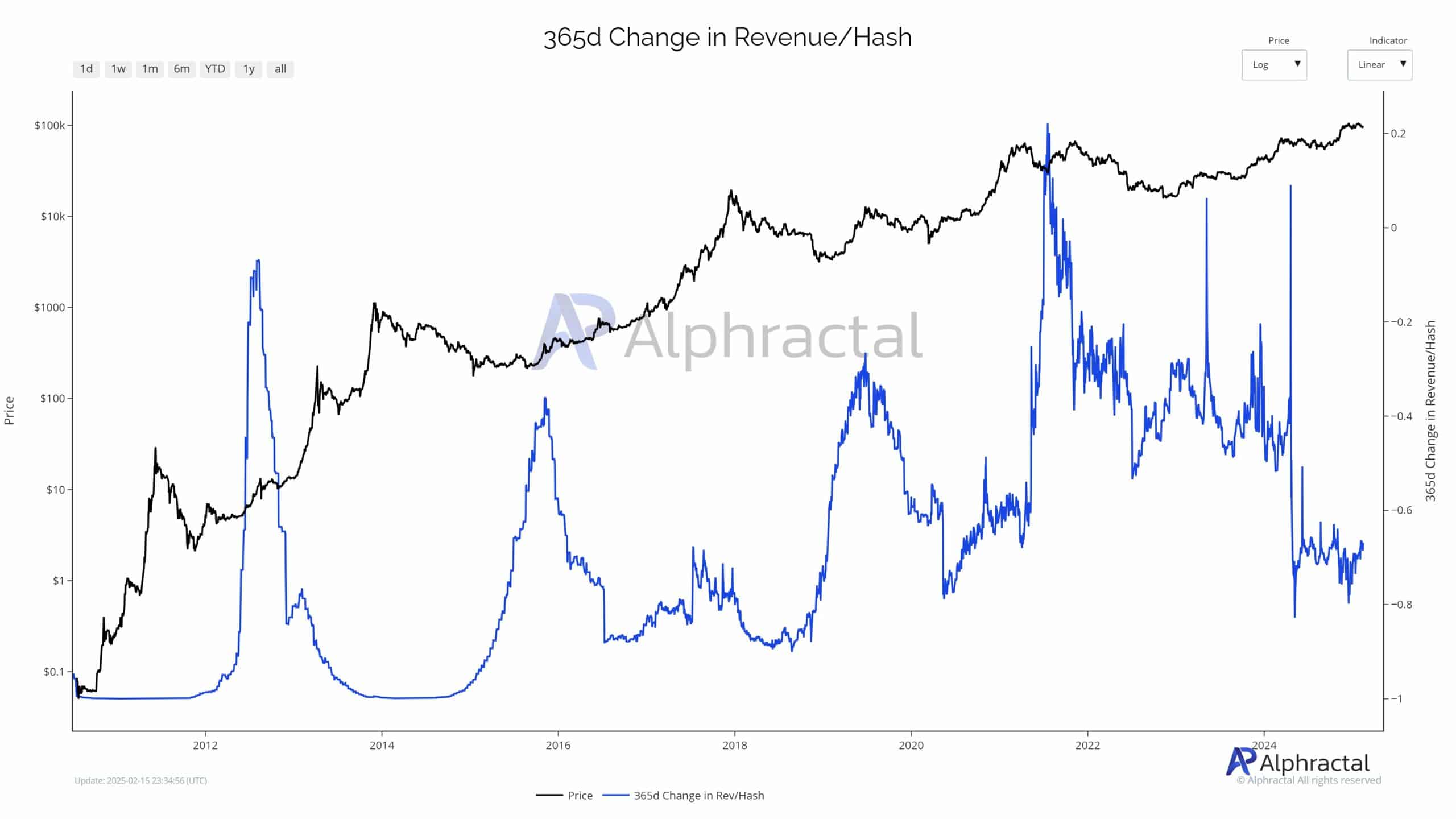
The Revenue/Hash ratio, a crucial measure for miners, currently stands at historic lows. Despite the increase in Bitcoin’s price, diminished returns highlight that growing network difficulty and competition have been reducing profitability.
With the halving event on the horizon, leading to reduced block rewards, smaller mining operations may struggle to maintain profitability.
This scenario may foster increased centralization, wherein only large, technologically capable miners continue to thrive, possibly driving smaller entities out of the market.
Growing Difficulty and Rising Operational Costs
Bitcoin miners are confronting an escalation in profitability pressures as network difficulty reaches new peaks.
The decreasing revenue per hash is making it increasingly difficult for smaller operators with outdated machinery to remain competitive, especially given the rising costs associated with energy and hardware.
To endure, many miners are relocating to areas with more affordable, sustainable energy options, such as hydro or geothermal sources.
Others are diversifying their income streams by entering the computing services sector, while some are pursuing mergers and acquisitions.
These strategies may contribute to further centralization within the industry, allowing only the best-resourced and most efficient mining firms to survive.
Such changes could affect Bitcoin’s decentralization, particularly concerning the geographical distribution of mining power.
Consequently, a transformation in Bitcoin’s security framework could emerge, raising doubts about the long-term sustainability of its decentralized nature.
Market Readjustments
As operational expenses escalate and profitability diminishes, Bitcoin’s hashrate may experience a natural decline, leading inefficient miners to cease operations.
This adjustment will likely leave only the most capitalized and technologically advanced players, reinforcing the mining sector as a high-entry barrier industry.
Nevertheless, this transition raises concerns regarding centralization. With a dwindling number of dominant miners, the decentralized principles of Bitcoin may be jeopardized, potentially concentrating network security within fewer entities.
While larger players may enhance stability, this consolidation could prompt concerns about censorship resistance and the overall trust in the network’s long-term integrity.
The 2024 halving has already tested the endurance of the Bitcoin mining ecosystem.
The period following this event is crucial for determining whether Bitcoin mining remains an equitable and competitive arena or if the industry continues to consolidate among a select few dominant entities.