Recent computer simulations carried out by scientists have examined the potential consequences of an asteroid impact on Earth, specifically one as large as the 500-meter-wide Bennu. The findings are alarming.
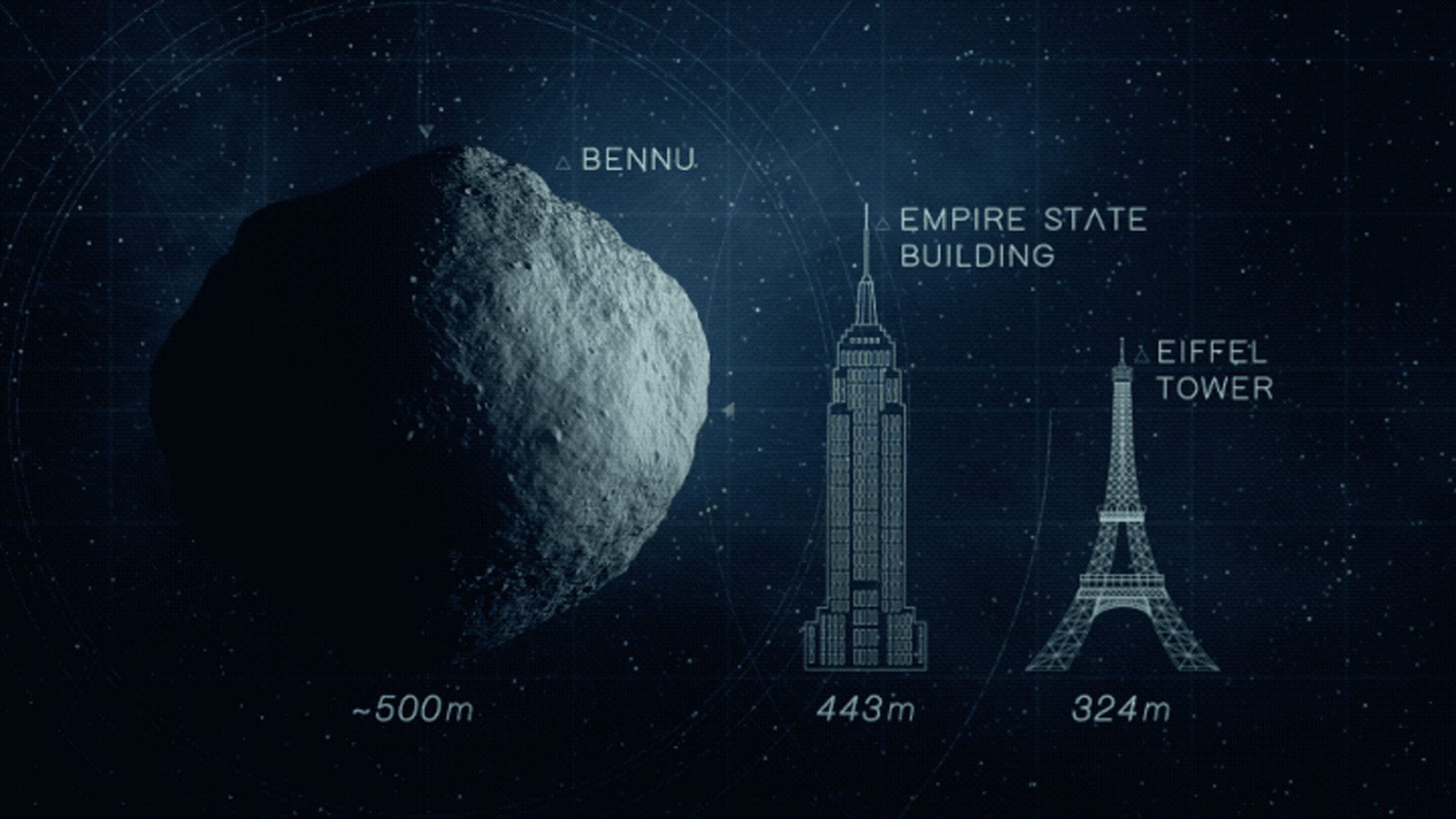
Why focus on Bennu? This asteroid, measuring approximately one-third of a mile at its widest point, has been assessed and found to have a 1 in 2,700 chance (or 0.037%) of colliding with Earth in 2182.
NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission recently targeted Bennu, marking the first U.S. effort to gather samples from an asteroid and return them to Earth, with a successful sample delivery in 2023. This asteroid was chosen due to its close approach, coming within about 186,000 miles—significantly closer than the moon—every six years.
The simulation results from the IBS Center for Climate Physics (ICCP) at Pusan National University highlight severe impacts from a potential strike by Bennu. If it were to hit, up to 400 million tons of dust could be released into the stratosphere, leading to substantial disruptions in climate, atmospheric chemistry, and global photosynthesis.
Projected global temperatures could plummet by 4°C (7°F), and precipitation levels could decrease by 15% as indicated by the simulations. Reportedly, the largest declines in primary productivity for both terrestrial and marine ecosystems could reach 36% and 25%, respectively.
“The iron content of the asteroid and the resulting marine dust deposition could trigger large diatom blooms in iron-limited areas, such as the Southern Ocean and eastern equatorial Pacific,” researchers noted.
But there’s more to consider.
A collision with Bennu would unleash thermal radiation, trigger earthquakes, generate tsunamis, and produce long-lasting climatic changes due to the release of aerosols and gases into the atmosphere.
“Dust causing solar dimming would lead to a sudden global ‘impact winter’ characterized by less sunlight, cooler temperatures, and reduced rainfall,” explained study lead author, Lan Dai, a postdoctoral research fellow at the IBS Center for Climate Physics.
The potential human cost of such an asteroid impact largely hinges on where it occurs, as per Dai’s insights.
However, a more immediate concern is the asteroid named 2024 YR4, which has a 1.2% likelihood of hitting Earth in 2032—the highest impact probability of any known large asteroid according to NASA. This situation is particularly troubling since, at this stage, we currently lack strategies to deflect it.
Moreover, we must also keep an eye on the massive 67.24 million ton asteroid referred to as the “Colossal God of Chaos,” which is expected to pass within 20,000 miles of Earth’s surface in 2029—closer than many satellites in orbit.