Paleontologists have unveiled a newly identified specimen of the genus Archaeopteryx, discovered within the Mörnsheim Formation located in Bavaria’s Franconian Alb region, Germany.

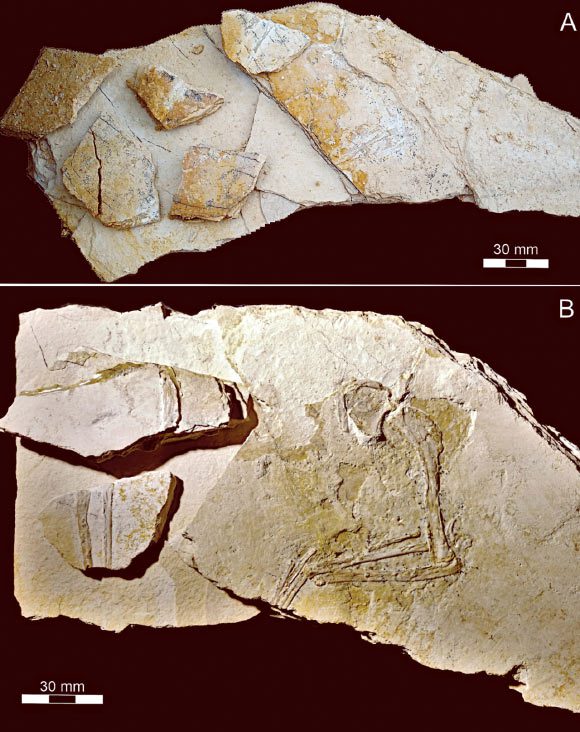
The Karlsruhe specimen: (A) original condition of the slabs prior to preparation; (B) slabs containing remains of the left arm and fragments of the right one post-preparation. Image credit: Foth et al., doi: 10.3897/fr.28.131671.
Archaeopteryx refers to a genus of feathered dinosaur-like birds that existed approximately 150 million years ago during the Jurassic era.
Currently, there are three recognized species and over ten specimens of Archaeopteryx known, all traced back to Bavaria, Germany.
As the earliest known bird, Archaeopteryx exhibited primitive characteristics, including teeth and a long bony tail, and its size was comparable to that of a Eurasian magpie.
“Archaeopteryx has been vital in discussions surrounding evolutionary theory in general and the evolution of birds specifically,” stated Dr. Christian Foth, a paleontologist from the University of Fribourg and Universität Rostock, along with his research team.
“This taxon is presently only identified from the lower Tithonian formation in Bavaria, Germany, with nine of the eleven known specimens belonging to this genus being excavated from the Altmühltal Formation.”
“Variations in morphology — such as in dental structure and limb proportions — imply that Archaeopteryx evolved over time and may have diversified into various species during that era.”
“For over 150 years, Archaeopteryx was the sole Jurassic representative classified as part of Paraves, a clade of theropods that includes modern birds and their closest relatives like dromaeosaurids and troodontids,” they noted.
“Recent decades have revealed a more varied assemblage of paravian theropods from slightly older geological formations in northeast China, separating the Haarlem specimen of Archaeopteryx as a distinct taxon, Ostromia crassipes, along with the identification of Alcmonavis poeschli, showcasing an unanticipated complexity in paravian evolution, diversity, and distribution during the Late Jurassic.”
The newly identified Archaeopteryx specimen—comprising a fragmentary skeleton—was unearthed in May 2019 from the Mörnsheim Formation in Mühlheim, Bavaria, southern Germany.
“This skeleton marks the third avialan specimen located within the Mörnsheim Formation,” the paleontologists explained.
“The findings include the right forelimb and shoulder as well as remnants of the left forelimb and both hind limbs.”
Colloquially known as the Karlsruhe specimen, this fossil is estimated to be around 149 million years old, making it the twelfth exemplification of the Archaeopteryx genus.
“The specimen falls within the size range of other recognized specimens, like those from Daiting, Munich, Thermopolis, and chicken wing specimens, classifying it as one of the medium-sized Archaeopteryx remains,” the researchers noted.
The findings were detailed in a research paper published in January 2025 in the journal Fossil Record.
_____
C. Foth et al. 2025. A new Archaeopteryx from the lower Tithonian Mörnsheim Formation at Mühlheim (Late Jurassic). Fossil Record 28 (1): 17-43; doi: 10.3897/fr.28.131671