Researchers from the University of Cambridge have introduced a groundbreaking solar-powered reactor that captures carbon dioxide (CO2) directly from the atmosphere and transforms it into a usable gas, potentially paving the way for a sustainable fuel solution. This cutting-edge technology presents an innovative approach to combating climate change by effectively removing harmful CO2 and generating clean energy simultaneously.
This advancement is especially timely as global initiatives to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and address climate-related issues continue to expand. Carbon capture and storage (CCS) has gained recognition as a viable strategy for reducing CO2 emissions; however, many current CCS methods depend on the combustion of fossil fuels for energy, rendering them ineffective in many aspects. Additionally, stored CO2 often requires deep geological placement, which raises concerns about long-term safety and logistical challenges.
Transforming CO2 into Valuable Resources
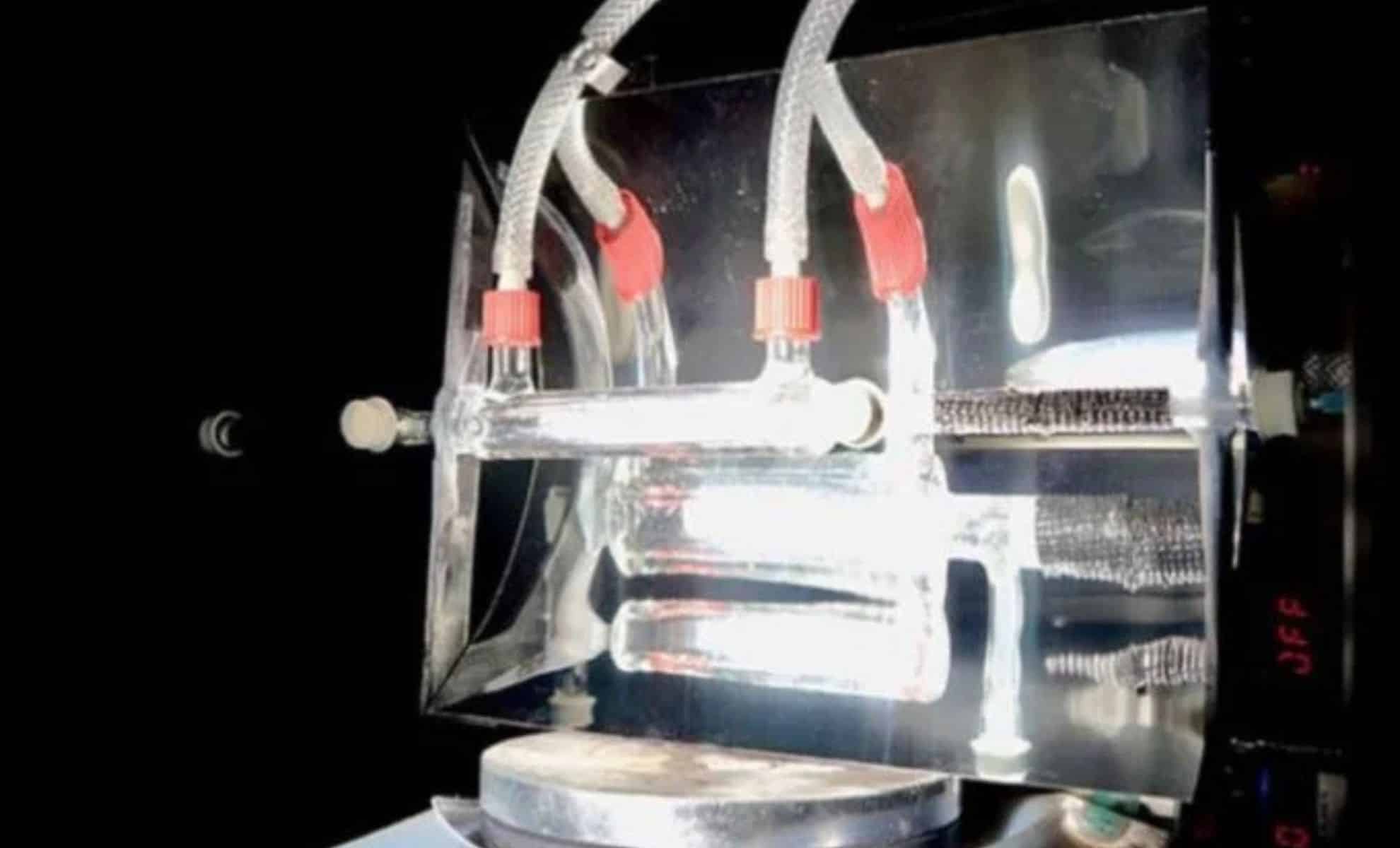
The team at the University of Cambridge has revolutionized carbon capture technology by asking a fundamental question: “Instead of burying carbon dioxide, what if we could create something beneficial from it?” This inquiry led to the development of a novel solar-powered reactor that converts CO2 into valuable chemicals and fuels while avoiding contributions to global warming. According to Sayan Kar, a chemist and lead author of the study, while CO2 is a harmful greenhouse gas, it also holds significant potential. The team’s approach enables the transformation of this environmental challenge into a resource for clean energy.
The research, published in Nature Energy in February 2025, outlines this pioneering work. The reactor uses solar energy to facilitate a chemical reaction. At night, it absorbs CO2 from the air, functioning like a sponge. During the day, sunlight heats the captured CO2, initiating a chemical reaction that converts it into synthesis gas (syngas), a mixture of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H2). This syngas can be leveraged to produce various fuels and chemicals, including those utilized in transportation and pharmaceuticals.
Addressing Two Major Global Challenges
The most impressive aspect of this innovation is its ability to tackle two critical challenges simultaneously. The reactor not only aids in removing CO2 from the atmosphere but also produces clean, renewable fuel that could serve as an alternative to conventional fossil fuels. As Erwin Reisner, the project leader from Kent, points out, “If we scaled up this technology, it could effectively address two issues: capturing CO2 from the atmosphere and creating a clean substitute for fossil fuels.” This approach paves the way for a circular, sustainable economy, viewing CO2 not as waste but as a resource for regeneration.
The findings suggest that this solar-powered system could be expanded to provide energy for off-grid locations. By generating energy in this innovative manner, the reactor could become a viable energy solution for remote or rural communities lacking established energy infrastructure. This positions the technology not only as a remedy for climate change but also as a way towards clean energy independence for individuals and areas in need.
Envisioning a Sustainable Future
This technological advancement ushers in the possibility of a sustainable, circular economy. “Rather than continuing our reliance on extracting and burning fossil fuels, we can directly capture CO2 from the atmosphere and repurpose it,” said Erwin Reisner. This vision of reusing captured CO2 to create sustainable fuels could signify a pivotal shift in humanity’s approach to climate change. Achieving this vision will necessitate political commitment and global cooperation. If adopted widely, these solar reactors could significantly aid in decarbonizing the energy and chemical industries while promoting a greener and more sustainable economy for future generations.