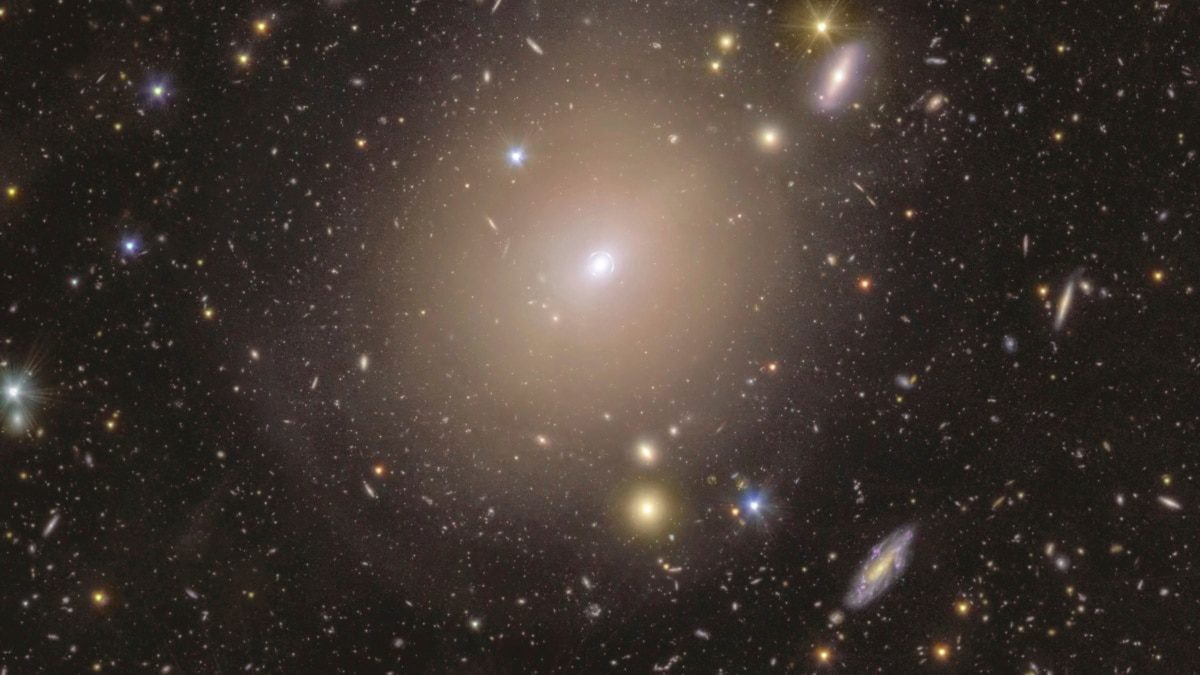
Researchers have announced a significant finding from Europe’s Euclid space telescope: a dazzling ring of light encircling a nearby galaxy. This observed phenomenon is referred to as an Einstein ring, a fascinating occurrence in the field of astrophysics.
The identified ring surrounds a galaxy located approximately 590 million light-years from Earth. A light-year represents the distance that light travels in one year, roughly 9.5 trillion kilometers.
Astronomers have been aware of the galaxy hosting this remarkable ring, known as NGC 6505, but were taken aback that such a pronounced ring had previously gone unnoticed. NGC 6505 is situated in the constellation Draco, a well-known group of stars.
Einstein rings are uncommon occurrences that manifest when light from a more distant galaxy bends around a galaxy that is closer to us. As a result, the nearby galaxy creates the appearance of a radiant halo of light around it.
The term “Einstein ring” honors the renowned physicist Albert Einstein, who predicted that light would curve around very massive objects in space, a phenomenon known as “gravitational lensing.”
NASA explains that as light navigates through a gravitational lens, it may follow various paths, leading to multiple images of the same celestial entity. In this manner, gravity acts as a lens, magnifying and distorting space-time similarly to optical lenses found in eyeglasses.
Utilizing gravitational lenses allows telescopes like Euclid to observe fainter, more distant celestial bodies. In this recent exploration, researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics analyzed data from Euclid to develop a computer model revealing the Einstein ring.
The Euclid space telescope, managed by the European Space Agency (ESA), was launched in 2023 for a six-year mission, aimed at unveiling the secrets of dark matter and dark energy throughout the cosmos.
Astronomers from the Max Planck Institute spearheaded this investigation. According to their statement, the initial indications of the Einstein ring’s existence surfaced during testing immediately after the deployment of Euclid. Team member Bruno Altieri reviewed early data collected by the telescope.
“Even from that first observation, I knew it was there,” Altieri remarked. “As Euclid gathered more data about the region, we clearly observed a perfect Einstein ring. For someone like me, who has a profound passion for gravitational lensing, this was nothing short of incredible.”
The scientists revealed that the more distant galaxy involved in this phenomenon is approximately 4.4 billion light-years away and has yet to be identified by name, making this discovery even more intriguing.
Altieri’s team has recently published their findings in a study featured in the journal Astronomy and Astrophysics .
Conor O’Riordan, another member of the team and the principal author of the study, stated, “All strong gravitational lenses hold significant scientific value due to their rarity. This particular lens is especially unique because of its proximity to Earth and its stunning alignment.”
O’Riordan further explained that the research team employed advanced gravitational lensing techniques developed at the institute to model the light emitted by the ring. “We even had to analyze some of the raw data to enhance our understanding of the detector mechanics.”
He indicated that their modeling efforts represent just the beginning of investigating the newly identified Einstein ring. Plans are in place to utilize the ring for further studies focused on “dark matter substructures” within the lensing galaxy.
O’Riordan anticipates, “Euclid is on the verge of revolutionizing the field, granting us access to unprecedented data.”
I’m Bryan Lynn.
Bryan Lynn authored this report for VOA Learning English, based on insights from The Associated Press, the Max Planck Institute, the European Space Agency, and NASA.
___________________________________________________
Terms to Know
galaxy – n. A vast assembly of stars held together within the universe.
bend – v. To curve or change shape.
distort – v. To alter the shape, sound, or appearance of an object.
lens – n. A curved piece of material used in cameras, glasses, and scientific instruments for focusing and viewing.
magnify – v. To enlarge the appearance of an object through specialized equipment.
perfect –adj. Flawless; without errors; entirely correct.
align – v. To arrange in a straight line or make parallel.
raw – n. Unprocessed or inadequately prepared for application.
detect – v. To discover or identify something, particularly if it is challenging to perceive.