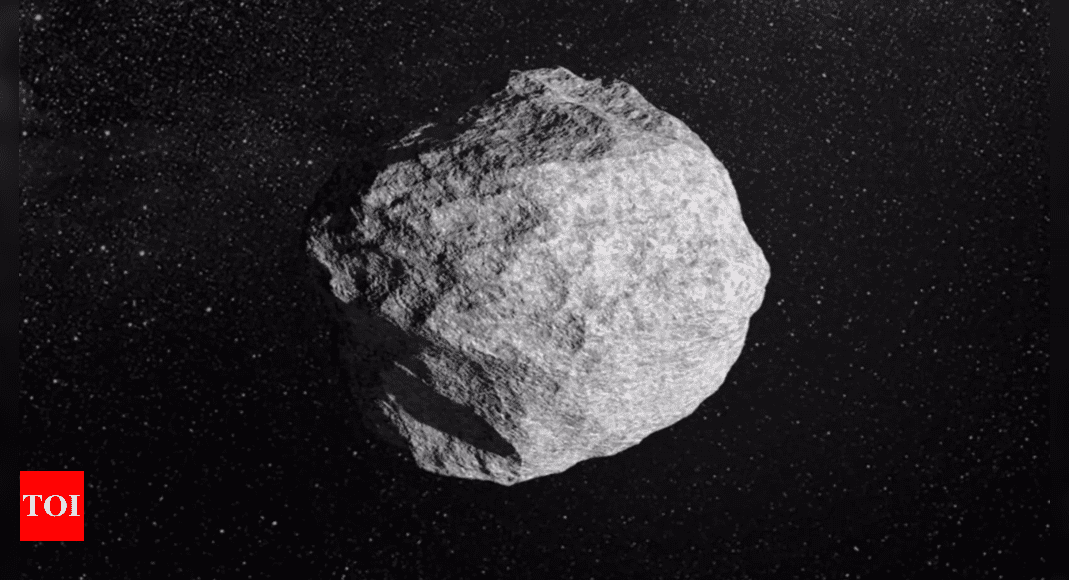
UK researcher Dr. Robin George Andrews, a volcanologist, has raised alarms regarding the potential impact of “city killer” asteroid 2024 YR4, which is currently on a path toward Earth. The asteroid has a one in 43 chance of colliding with our planet in 2032. If it impacts land, its size—comparable to the Leaning Tower of Pisa—could lead to devastating consequences. Conversely, if it were to land in the ocean, the repercussions would likely be less severe.
Asteroid YR4 was first identified in December 2024 and currently holds a Torino Scale rating of 3 out of 10. NASA plans to utilize the James Webb Space Telescope to monitor its trajectory and characteristics. The asteroid is expected to be at its most visible in March 2025, during the initial round of observations. A follow-up observation will occur in May as YR4 moves away from the Sun, providing a crucial chance for study before it returns in 2028.
Dr. Andrews pointed out that while the Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) successfully altered the course of a 580-foot-wide asteroid in 2022, this does not imply that every asteroid can be redirected on command.
He elaborated, “The first concern is that many asteroids, like Dimorphos, consist of loosely bound rubble rather than solid mass. If struck improperly, these can shatter instead of being redirected. Hitting an asteroid too hard might result in many fragments heading toward Earth. It’s akin to turning a cannonball into a scatter shot,” he noted.
“Accidental disruption of an asteroid is dangerous, as the resulting debris could still pose a threat to our planet. This is a highly unpredictable situation, and if DART had struck Dimorphos with more force, it could have fragmented instead of successfully deflecting it.”
Additionally, Dr. Andrews clarified that although DART achieved a noticeable decrease in Dimorphos’ orbit, the actual change in velocity was only 2.7 mm/s. “The orbital reduction sounds significant, but the amount Dimorphos actually moved was minimal,” he concluded.