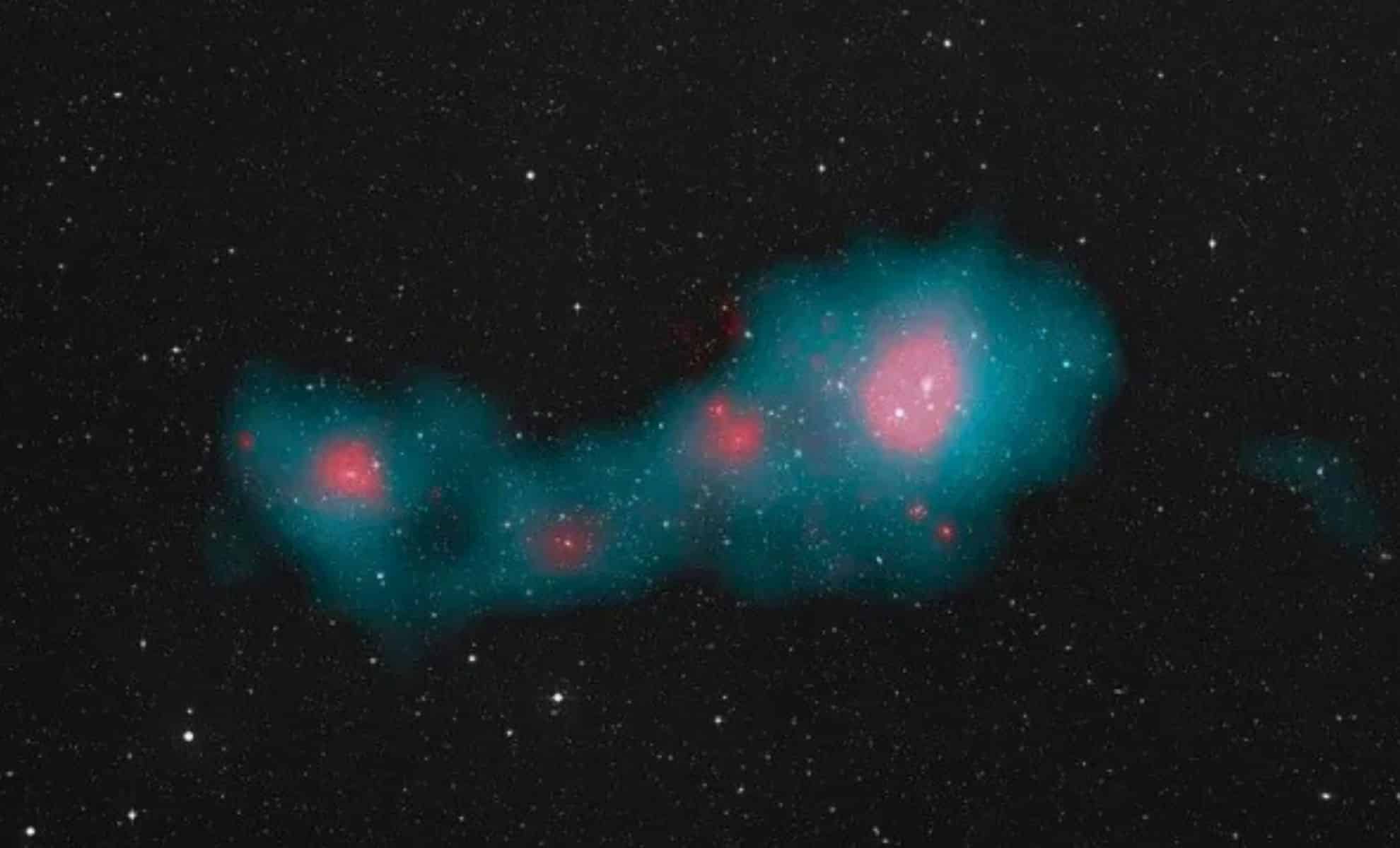
Astronomers have made a groundbreaking discovery of an extraordinary cosmic titan. This remarkable structure, known as Quipu, comprises a massive filament of galaxies that spans approximately 1.3 billion light-years, making it the largest known formation in the universe. Drawing its name from the Incan counting system that used knotted cords, Quipu houses a staggering 200 quadrillion solar masses and stretches over 13,000 times the length of our Milky Way galaxy.
Unveiling Quipu: A Colossal Cosmic Giant
Quipu is much more than just a supercluster; it represents a superstructure of interconnected galaxy clusters and filaments that forms an elaborate network extending beyond a billion light-years. Unlike conventional galaxy clusters, which are tightly bound by gravitational forces, Quipu features a long central filament with numerous branching filaments, resembling a woven cord.
This colossal structure was identified not through standard detection methods, but became immediately apparent in sky maps focused on a specific redshift range of galaxy clusters. The research team observed that Quipu was prominently visible, highlighting its remarkable significance in the cosmic landscape.
A New Classification of Cosmic Behemoths
Prior to this finding, the largest known cosmic formations included:
- Laniākea Supercluster – Home to our Milky Way, this immense region of galaxies spans about 500 million light-years.
- Shapley Supercluster – Once regarded as the largest known structure, this is one of the densest and most massive superclusters.
- The Hercules-Corona Borealis Great Wall – A vast group of galaxies located about 10 billion light-years away, covering an enormous distance, though its existence is still up for debate.
However, Quipu and four newly discovered cosmic formations surpass the Shapley Supercluster, significantly enhancing our understanding of the large-scale distribution of matter within the universe.
The five newly classified superstructures include:
- Quipu (in red) – The largest filamentary structure ever uncovered.
- Serpens-Corona Borealis superstructure (in green) – Another major formation stretching through these constellations.
- Hercules supercluster (in purple) – A densely populated galactic region with a powerful gravitational influence.
- Sculptor-Pegasus superstructure (in beige) – A vast structure connecting these two notable constellations.
- Shapley Supercluster (in blue) – Once the largest known entity, now overshadowed by Quipu and its peers.
Collectively, these structures contain 45% of all recognized galaxy clusters, 30% of observable galaxies, and 25% of the matter in the known universe. They occupy 13% of the observable universe’s volume, solidifying their critical role in the evolution of cosmic structures.


How Did Astronomers Uncover Quipu? A Map of the Cosmic Web
The identification of Quipu emerged from a sophisticated redshift mapping survey, concentrating on galaxy clusters within a redshift range of 0.3 to 0.6. The higher the redshift, the more distant (and therefore more ancient) these structures are. Most larger-scale surveys had focused exclusively on objects within redshift 0.3, overlooking deeper cosmic structures.
By broadening their search criteria, scientists uncovered Quipu and its neighboring formations, suggesting the potential for even larger structures beyond our current observational limits.
Understanding the Redshift Technique: Peering into the Depths of the Universe
Redshift occurs as the expanding universe stretches light’s wavelength, pushing it toward the red end of the spectrum. By measuring these shifts, astronomers can gauge the distance and velocity of galaxies, aiding in the construction of a three-dimensional map of the cosmos.
Quipu: A Transient Giant in the Cosmic Timeline
Even with its colossal dimensions, Quipu is not a permanent fixture. The universe continues to expand, and over time, these massive filaments will disperse. While gravity keeps them bound currently, as dark energy accelerates this cosmic expansion, the filaments will gradually unravel, leading to the separation of galaxies.
The Future of Quipu and the Cosmic Web
- Over the coming billions of years, Quipu will fragment into smaller clusters as cosmic expansion stretches the fabric of space itself.
- Galaxies within Quipu will drift apart, ultimately becoming isolated island universes.
- Future astronomers (if any remain) may find it impossible to detect these superstructures as the cosmic web begins to dissolve.
Looking Ahead: The Quest for Even Larger Structures
While Quipu currently reigns as the largest known cosmic structure, astronomers speculate that even more colossal formations might exist deeper within the vast reaches of space. The further advancement of telescope technology, including instruments like the James Webb Space Telescope and the upcoming Euclid mission, may extend redshift mapping beyond 1.0, potentially uncovering structures that span hundreds of billions of light-years.
This remarkable finding, detailed in a recent study on arXiv, challenges our comprehension of large-scale cosmic formations and brings forth fundamental inquiries regarding the evolution and structure of the universe. For the moment, Quipu remains a stunning testament to the vastness and intricacy of the cosmos—an immense, interconnected web that extends across billions of light-years, holding secrets from our universe’s distant past.
This article has been adapted from the following sources. Please note that material may have been edited for length and clarity. For additional information, please refer to the original source.
Have any thoughts to share? Join the conversation in the comments
Liked this article? Subscribe to our free newsletter for engaging narratives, exclusive content, and the latest updates.